Also known as bio hazards, refer to biological substances that pose a threat to the health of living organisms, primarily that of humans. This can include medical waste or samples of a microorganism, virus or toxin (from a biological source) that can affect human health. It can also include substances harmful to other animals.

Some Examples of Biohazards Are:
- Human blood and blood products: This includes items that have been contaminated with blood and other body fluids or tissues that contain visible blood.
- Animal waste: Animal carcasses and body parts, or any bedding material used by animals that are known to be infected with pathogenic organisms.
Human body fluids: Semen, cerebrospinal fluid, pleural fluid, vaginal secretions, pericardial fluid, amniotic fluid, saliva, and peritoneal fluid. - Microbiological wastes: Common in laboratory settings, examples of microbiological wastes include specimen cultures, disposable culture dishes, discarded viruses, and devices used to transfer or mix cultures.
- Pathological waste: Unfixed human tissue (excluding skin), waste biopsy materials, and anatomical parts from medical procedures or autopsies.
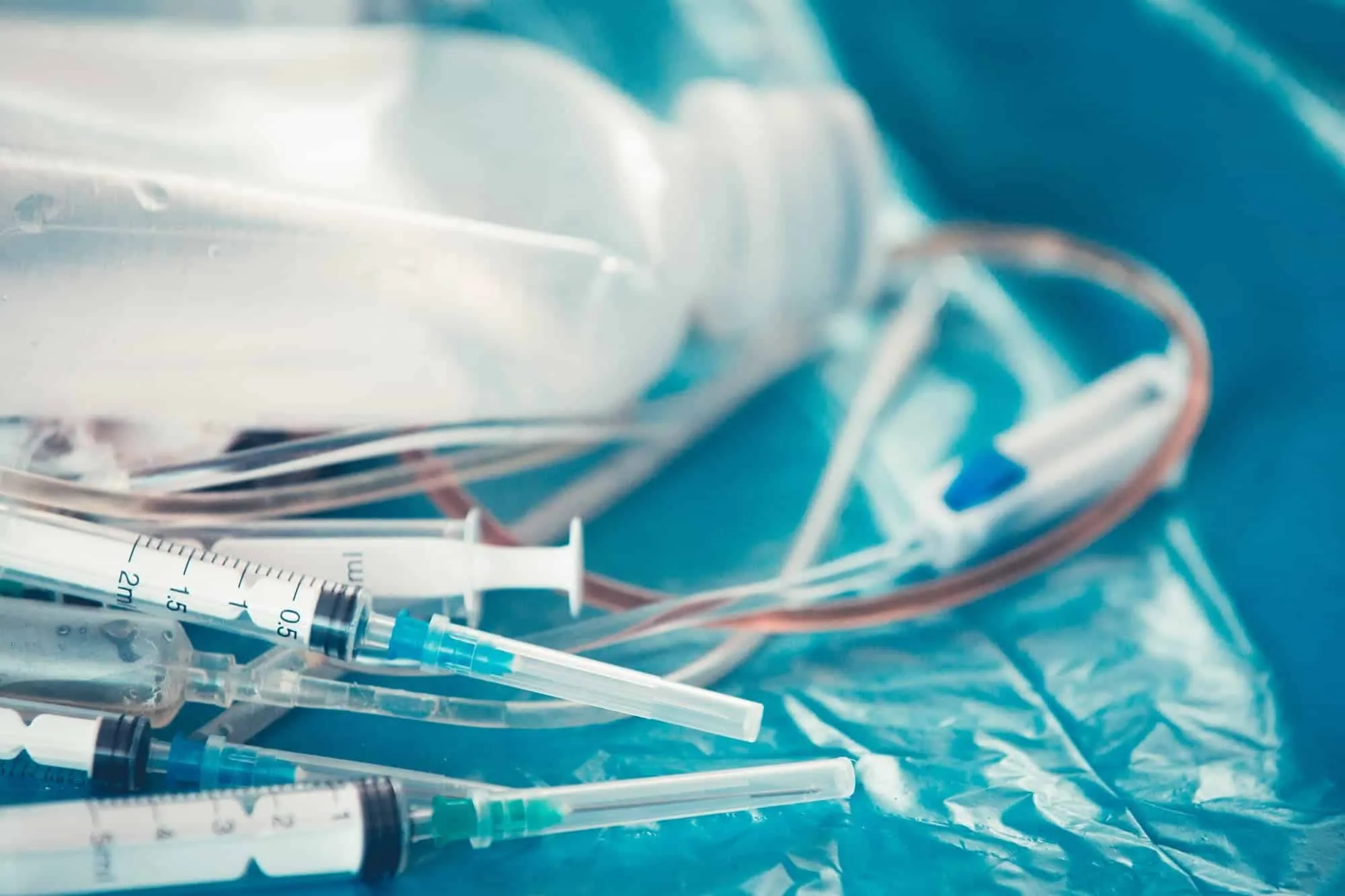
- Sharps waste: Needles, glass slides and cover slips, scalpels, and IV tubing that has the needle attached.